Mastering BCBS 239: The Path to Unified Risk Data Management
Discover how adhering to the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision’s standard (BCBS 239) can revolutionize your risk management. Learn everything from the basics, its significance under current economic conditions, and how Aryza’s Unified BCBS 239 Solution can future-proof your financial institution.
The Importance of Risk Management under Current Economic Conditions
In today’s economic climate, characterized by uncertainty and rapid changes, implementing an effective risk management is more critical than ever for banks. In the aftermath of crises, regulators and stakeholders have heightened expectations for transparency, accountability, and prudent management of financial risks.
BCBS 239 serves as a foundation for banks to build these capabilities, aligning their operational practices with the needs of a stable, resilient financial system.
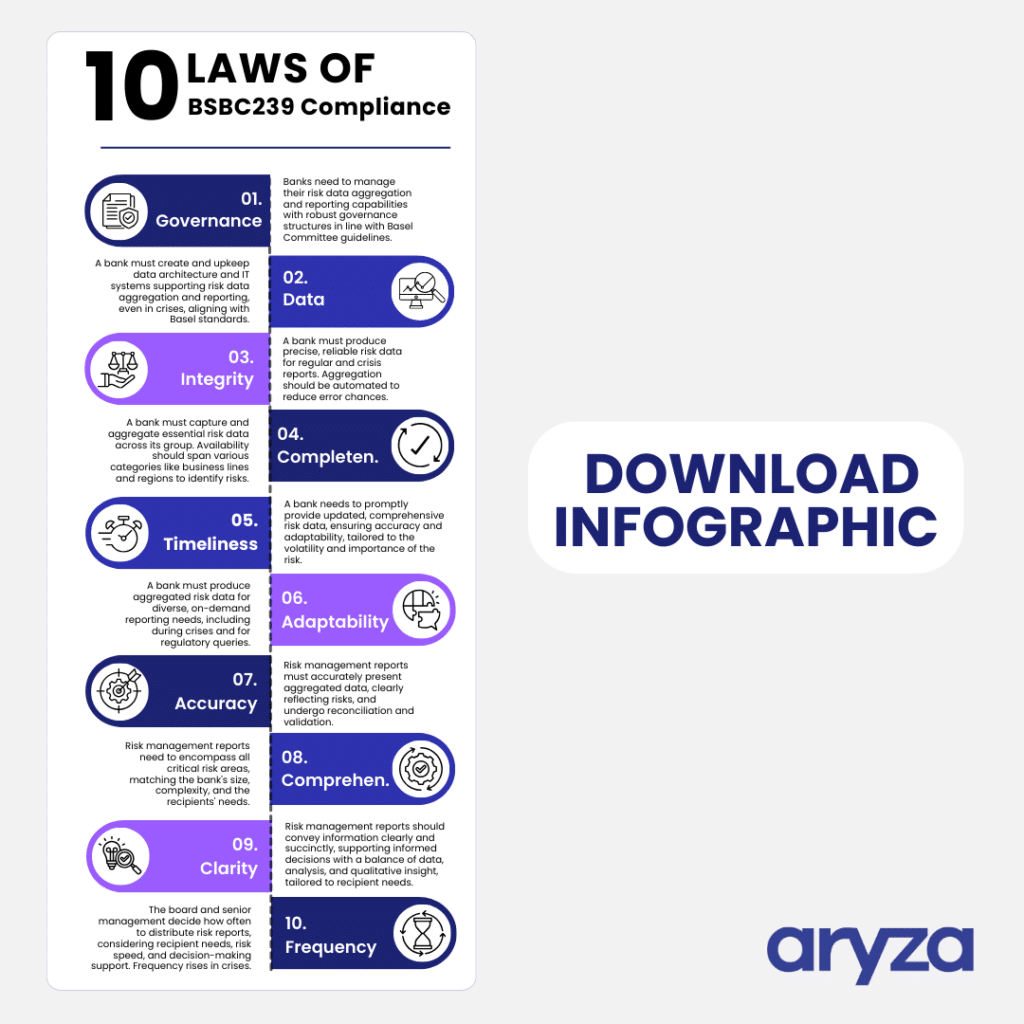
Effective implementation of BCBS 239 enables banks to:
- React more quickly to financial crises, by having reliable risk data that can be aggregated swiftly and efficiently.
- Make informed decisions, thanks to comprehensive risk reports that provide a clear picture of the bank’s risk exposure.
- Meet regulatory requirements, thus avoiding potential fines and sanctions from regulatory bodies.
- Enhance investor confidence, by demonstrating robust risk management practices and compliance with international standards.
About BCBS 239
BCBS 239 aims to enhance banks’ risk management, yet many still struggle with its full implementation due to data quality issues.
BCBS 239 stands for the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision’s standard number 239, titled “Principles for effective risk data aggregation and risk reporting.” This standard, published in January 2013 and applicable from January 1, 2016, for Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs), aims to strengthen banks’ capabilities in aggregating risk data and improving internal risk reporting practices. This, in turn, is expected to enhance risk management and decision-making processes within banks.
A noteworthy point is that as of a May 2018 report by the European Central Bank, none of the 25 significant institutions – some classified as G-SIBs – had fully implemented the BCBS 239 principles. The challenges were primarily due to ambiguities around responsibility and accountability for data quality.
Understanding BCBS 239: The Framework Components
BCBS 239 is not just about improving risk data aggregation and reporting; it’s about creating a robust framework that banks can use to enhance their decision-making and risk management processes. This standard is intricately linked to other financial regulations and frameworks.
Implementing BCBS 239 requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses various types of information, data, and standards.
The key components needed:
Information and Data
- Risk Data: Detailed and up-to-date information on all relevant risk types, including credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk. This includes data on transactions, positions, portfolios, collateral, and historical losses.
- Exposure Data: Information on the bank’s total exposures to individual counterparties or market movements, including off-balance-sheet positions, derivatives, and other risk-bearing instruments.
- Financial Data: Balance sheet data, income statements, equity information, and other financial metrics necessary for risk assessment and capital management.
- Macroeconomic Data: Information on economic indicators, market trends, and other external factors that could influence the bank’s risk position.
Standards and Frameworks
- Data Architecture and IT Infrastructure: A robust data architecture and IT infrastructure are crucial for supporting efficient data collection, processing, and reporting. This includes systems for data management, data quality controls, and data integration.
- Governance and Policies: Clear governance structures, including responsibilities and accountabilities for risk management and data reporting. Policies for data access, data privacy, and data security are also essential.
- Analytical Models and Methods: Advanced models and analytical methods for assessing various risk types, such as calculating Probability of Default (PD), Loss Given Default (LGD), and Exposure at Default (EAD).
- Reporting Standards: Standards for risk reporting that ensure reports are accurate, comprehensive, and timely. This includes adherence to international accounting standards like IFRS 9.
Connection to Other Financial Standards
- IFRS 9: Requires banks to record expected credit losses and update the amount of expected credit losses recognized at each reporting date. The implementation of BCBS 239 supports meeting these requirements by providing accurate and timely risk data.
- Basel III/IV: Includes regulations for capital requirements and liquidity standards. BCBS 239 enhances banks’ ability to accurately measure their risk positions and hold appropriate capital.
- ESG Guidelines: Growing importance of Environmental, Social, and Governance factors in banking. BCBS 239 can help structure the collection and analysis of ESG-related risk data.
Principles for effective data aggregation and risk reporting were published back in 2013. Some delays are understandable, as banks may need to make major changes to existing IT infrastructure to resolve the issues, but it is crucial that they have a clear action plan in place with verifiable milestones. This requires the right data to be able to take the right decisions.
Edouard Fernandez-Bollo, Member of the Supervisory Board of the European Central Bank, 20 February 2024.
Implementing Unified BCBS 239 Risk Data Management
Aryza’s Unified BCBS 239 Risk Solution aims to optimize risk management, ensure compliance, and boost efficiency by eliminating superfluous processes.
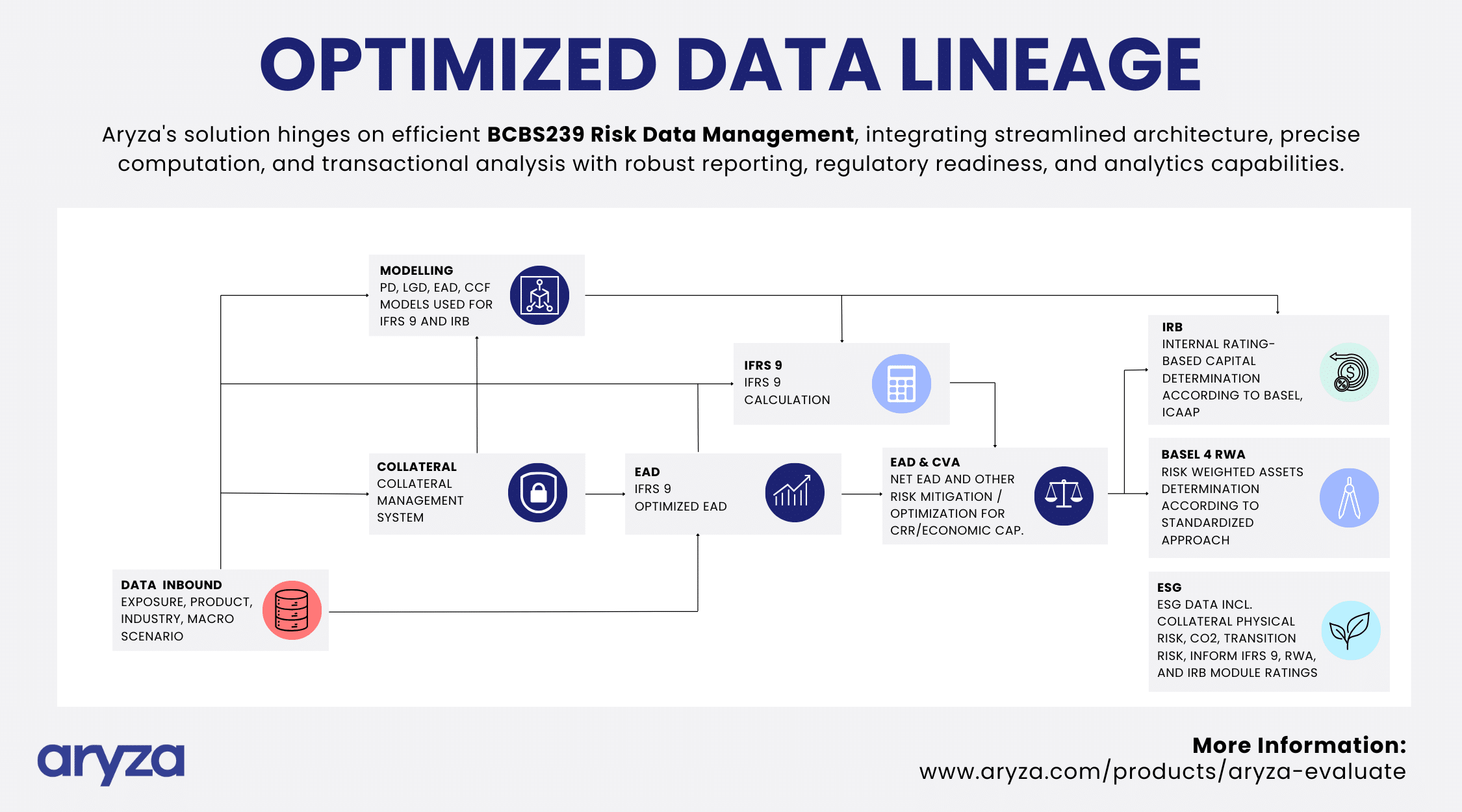
Core Components of Aryza’s Risk Data Management System
Data Collection and Analysis: At the system’s heart lies the thorough collection of data on exposures, products, industries, and macroeconomic scenarios. This foundation supports sophisticated analyses and modeling for Probability of Default (PD), Loss Given Default (LGD), Exposure at Default (EAD), and Credit Conversion Factor (CCF), underscoring the interconnectedness of data and its impact on compliance with IFRS 9 and Basel III’s IRB approach.
Collateral Management / Risk Mitigation: A key strategy for minimizing credit risk, leading to optimized Exposure at Default (EAD) for IFRS 9 compliance and RWA optimisation. This approach is intricately linked to subsequent steps of risk mitigation and compliance, demonstrating the system’s seamless integration and the critical flow of data across processes.
System Benefits
Regulatory Compliance / Strategic Decision-Making: The Aryza system provides a robust framework for determining internal rating-based capital according to Basel, calculating risk-weighted assets, and incorporating SG data for physical, CO2, and transition risks. It’s designed not as a series of standalone tasks but as a unified approach essential for IFRS 9, RWA, and IRB module ratings.
Enhanced Resilience / Future Readiness: By streamlining process efficiency and strengthening risk management practices, our system not only meets current regulatory demands but also positions financial institutions for long-term success and stability. This is key to turning risk management into a strategic advantage, preparing them for future challenges and opportunities.