Stay Ahead of ECB Regulations:
Mastering Risk Data Management
The ECB has published a guide outlining that data quality requirements are essential for the quantification of risk, analysis and decision-making: Serving as a key building block of the ECB’s 2023-25 work programme, these regulations increase pressure on the management bodies of banks and lending organisations. The consequences for non-compliance are severe.
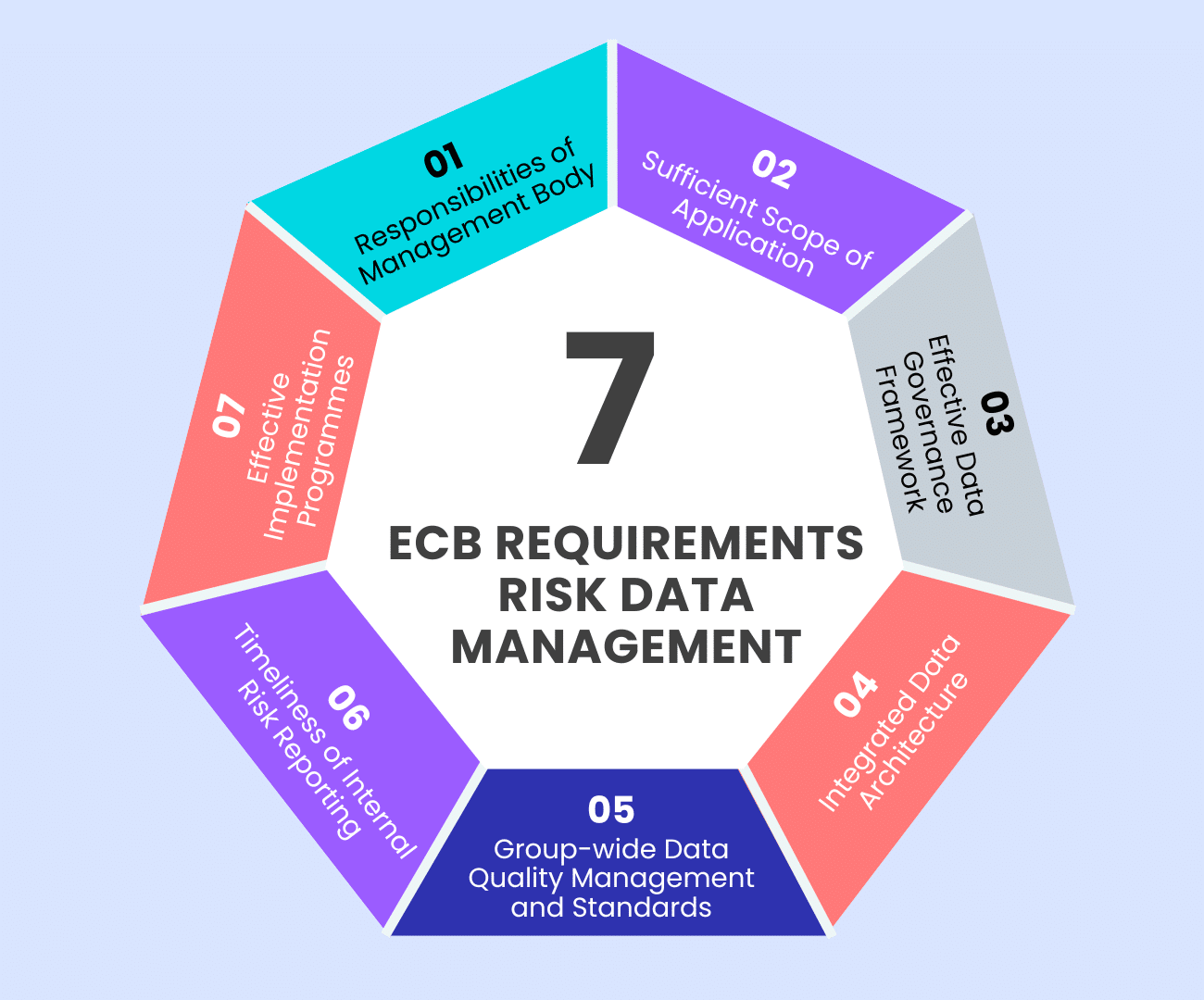
ECB Requirements
7 Risk Data Management Rules
In its ,guide on effective risk data aggregation and risk reporting’ the Banking Supervision is not shy about criticism: “Institutions are still focusing on the cost and implementation challenges […] rather than the benefits of remedying long-standing deficiencies in this area.”
The ECB points out deficiencies in the “Regulations on Data Asset Registration and Reporting” (RDARR). According to the authority, many institutions are still far from the required target state.
The ECB has therefore developed a comprehensive, targeted supervisory strategy for 2023-2025 to address these issues and expects institutions to assess whether their data governance frameworks comply with the applicable legal framework.
Implementation Step 1
Data Management and Compliance
The right Metadata is key for a Unified Risk Data Management. It tells data governance where the data comes from, what happens to it, and how it’s used. Individual business policies regarding who is responsible for data quality and how data is classified, stored, protected, and used can then be enforced by the institution’s supervisors.

Implementation Step 2
Data Automation Features and Solutions
To enforce data management policies and maintain long-term compliance with standards, technology is recommended. It can significantly reduce manual work and operational risks by automating tasks.
There are multiple features available on the market, some “Must-Haves” and some “Nice-to-Haves”, depending on the needs of the company.
Must-Haves
These automated features are essential for effective data management, especially for organizations that deal with large volumes of data, have compliance obligations, or require high data integrity:
- Extraction/discovery of metadata: Crucial for understanding and utilizing data correctly, especially for governance and compliance.
- Building data lineage: Vital for tracking data origin, transformation, and usage, which is important for audits, compliance, and understanding data dependencies.
- Classification of data: Important for compliance with data protection regulations (like GDPR) and for securing sensitive information.
- Audit trails and history: Necessary for compliance and for understanding changes and modifications made to data over time.
- Measurement and monitoring of data quality: Critical for ensuring data accuracy and reliability, which affects decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Reporting on data management KPIs: Essential for monitoring the effectiveness of data management practices and for strategic decision-making.
Nice-to-Haves
These features enhance functionality and user experience but may not be critical for basic data management needs:
- Notifications: Useful for keeping relevant stakeholders informed and ensuring timely actions on data-related tasks, but not critical unless specific workflow or compliance requirements exist.
- Anomaly detection through data profiling: Enhances data integrity by identifying outliers or errors but is not essential unless the organization has high data accuracy needs.
- Data cleansing processes: Helpful for maintaining data quality but may not be necessary for organizations with less stringent data quality requirements.
- Self-service capabilities: Beneficial for empowering users and reducing dependency on data teams, but not a core requirement for data management functionality.
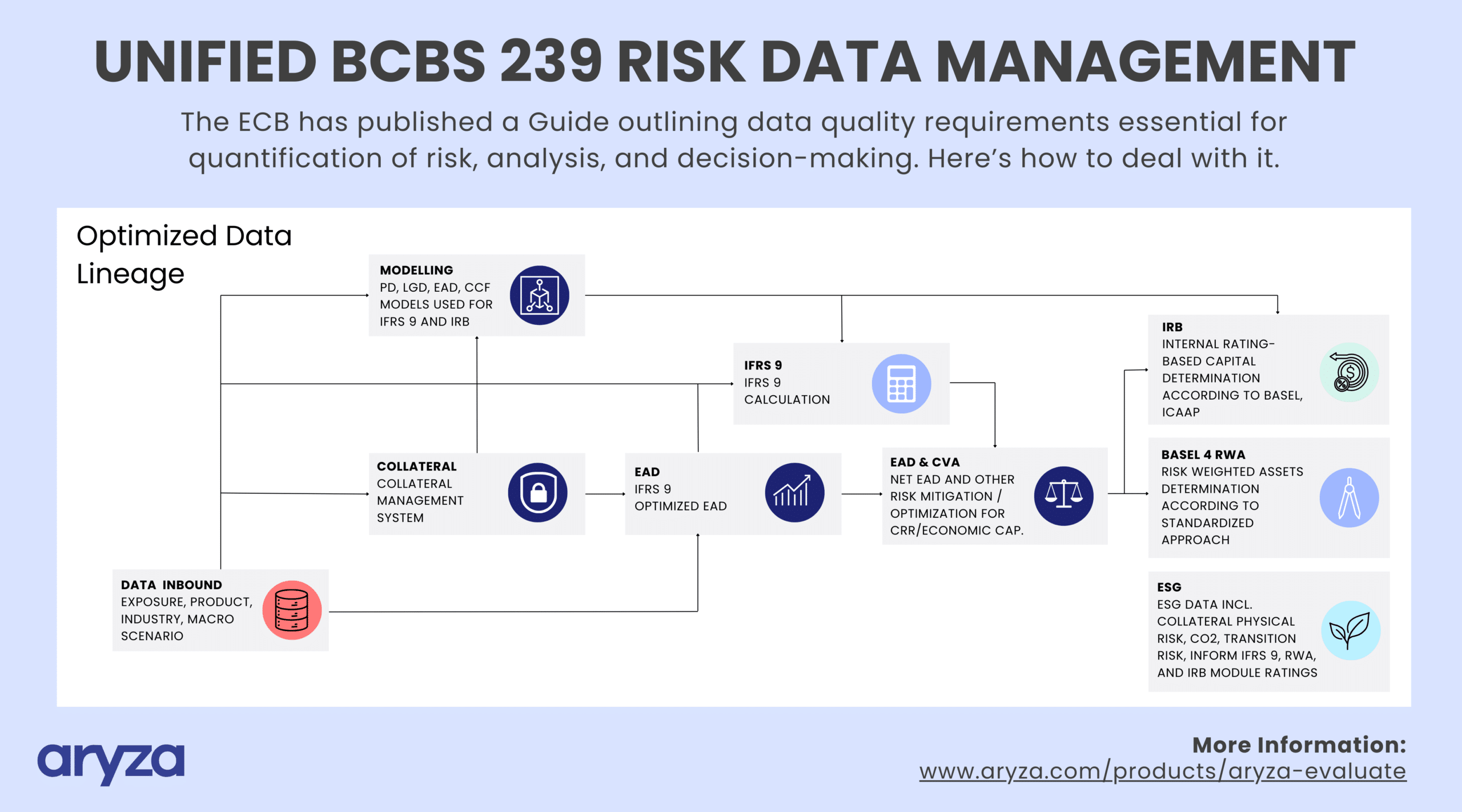
Implementation – Step 3
The Aryza Approach
Aryza’s implementation approach for enhancing risk data management involves a series of structured steps. Data transformation, as a product of calculations, must ensure any newly created data from the original source is explained and archived, detailing where the data comes from, what happens to it, and how it’s used.
These steps are designed to ensure the effective setup and integration:
-
Business Data Catalog Compilation: The process begins with the creation of a Business Requirements Specification (BRS) document. This document thoroughly assesses each data item necessary for integrating into the risk data aggregation framework.
-
Technical Level Catalog Development: From the initial BRS, a system requirements specification (SRS) documents is derived. It specifies which IT systems host the required data, outlines the data’s structure, and includes mappings linking data items from the BRS to those in the SRS.
-
Logical Data Model Design:
In a subsequent step, the Logical Data Model (LDM) for the risk data hub is designed to effectively accommodate all the collected data. -
Physical Data Model Design: A Physical Data Model (PDM) is crafted to ensure optimal physical storage and retrieval of data within the risk data hub.
-
System Interfaces Design: Interfaces between the various systems involved in the data feed process are designed and specified. This step involves creating SRS documents for each source system and the connections between sources and the data hub.
-
Documentation of Data Transfer Processes:
Detailed documentation outlines each step of the data transfer processes from their sources to the risk data hub. This includes assessments of potential data corruption risks at each transfer point, whether involving simple data movement or transformation. -
Analysis of Data Dependencies and Bottlenecks: An analysis is conducted to identify any dependencies and bottlenecks in the data transfer or processing steps. This analysis aids in optimizing and parallelizing the feed process to ensure the timely availability of risk data to stakeholders, typically by the next business day.
Effective risk data management is crucial for informed decision-making and compliance with ECB regulations. By leveraging advanced technology and a structured implementation approach, we ensure data integrity, compliance, and accessibility across the organization.
Sanjin Bogdan, Head of IFRS 9 Aryza